Faraday Calculator is a calculation sheet to solve problems of the Faradays law of electrolysis.
This software solves the problem not as a black box but as a white box. You need to think the process of solving a problem. This makes your knowledge refresh. The black box solution is convenient, however it has a risk of losing your knowledge. This software has few such risks.
A typical problem is as follows.
(Example)
A factory is planning to produce aluminum by 1000kg a day.
How much current is needed?
//Step 0: Preparation//
Prepare chemical equations and atomic (molecular) weights.
This chemical equation needs to include electrons to determine z value.
They are as follows.
Al3+ + 3e- -> Al
Determine substance and z value. The z value is the number of electrons reacting to one substance particle.
The substance is Al and the z value is 3, since three electrons are reacting to one Al particle.
Atomic weight of Al = 26.98 [g/mol]
//Step 1: Definition//
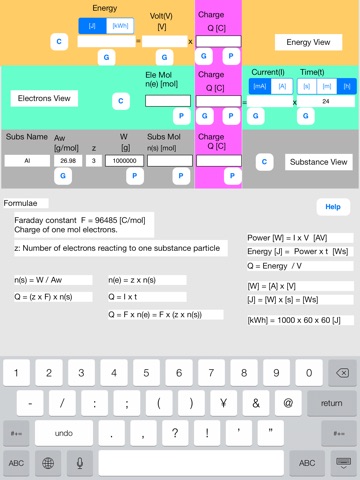
Enter known data into the Fdy sheet.
The upper row corresponds to data of energy.
The middle row corresponds to data of electrons.
The lower row corresponds to data of substance.
Lower row
Name = Al, Aw = 26.98, z = 3, W = 1000000
Middle row
Time(t) = 24[h]
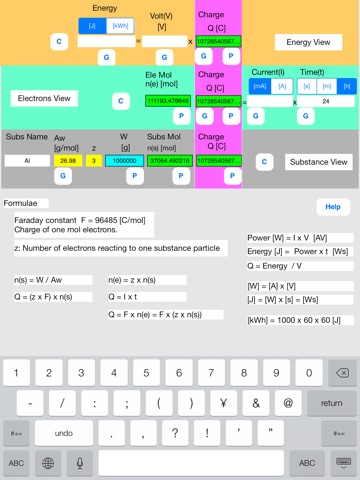
//Step 2: Calculation//
Data are not independent but mutually related by formulae.
Calculation is a conversion from unknown data to known data using the formulae.
The formulae are embedded in P and G buttons.
Touching out those buttons executes the formulae and changes unknown data to known data.
Touch out buttons as follows.
Touch out P_W button of the lower row. All charge data are changed to known data.
Set current unit to [A].
Touch out G_current button of the middle row. Current data is changed to known data.
It turns out that the needed current is 124173 A, i.e. 124 kA.
[Data label]
Lower row
Subs Name: Substance name.
Aw [g/mol]: Atomic or molecular weight of substance.
z: number of electrons reacting to one substance particle.
W [g]: Substance weight.
Subs Mol n(s) [mol]: Substance mol quantity.
Charge Q(s) [C]: Substance charge
Middle row
Ele mol n(e) [mol]: Electrons mol quantity.
Charge Q(e) [C]: Electrons charge
Current(I) [mA][A]: Current.
Time(t) [s][m][h]: Time
Upper row:
Energy [J][kWh]: Electric power for electrolysis when the loss is zero.
Volt [V]: Voltage impressed to the substance.
Charge Q [C]: Charge.
[Buttons and data]
//P button and P data group//
P (put) button inputs data to which the P button is assigned.
P data group is a group of data to which the P buttons are assigned. The P data group has a special character. When one P data is input, all other data of the P data group are updated by formulae.
//G button//
G (get) button gets data from other data using the formulae.
//C button//
C (Clear) button clears all data.
[Color change]
Touching out a button executes calculation and generates output data from the input and the referenced data. Unknown data are changed to known data.
Color change shows what data are input, output, or referenced data in this button execution.
Input data:Blue color
Referenced data:Yellow color
Output data:Green color
Uncalculated data:Red color
Referenced data is an input data that is referenced at the P button execution.
Uncalculated data is an output data that is not normally calculated. This uncalculated data is not output. The former data is remains unchanged in this data field.
[Formulae]
Embedded formulae are as follows.
F = 96485 [C]
n(s) = W / Aw
Q = (z x F) x n(s)
Q = I x t
n(e) = z x n(s)
Q = F x n(e) = F x (z x n(s))
Power [W] = I x V [AV]
Energy [J] = Power x t [Ws]
Q = Energy / V
[W] = [A] x [V]
[J] = [W] x [s] = [Ws]
[kWh] = 1000 x 60 x 60 [J]